P.A.D.
Peripheral Artery Disease
P.A.D. is a disease in which plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to your limbs. The plaque buildup, or atherosclerosis, can harden and limit blood flow. The limited blood flow can cause many symptoms. If the blockage remains in the peripheral arteries in the legs, it can cause pain, changes in skin color, sores or ulcers and difficulty walking. Total loss of circulation to the legs and feet can cause gangrene and loss of a limb.
What are the symptoms of P.A.D?
Symptoms include but are not limited to:
- Painful cramping in your hip, thigh or calf muscles after activity, such as walking or climbing stairs (intermittent claudication)
- Leg numbness or weakness
- Coldness in your lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side
- Sores on your toes, feet or legs that won't heal
- A change in the color of your legs
- Hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs
- Slower growth of your toenails
- Shiny skin on your legs
- No pulse or a weak pulse in your legs or feet
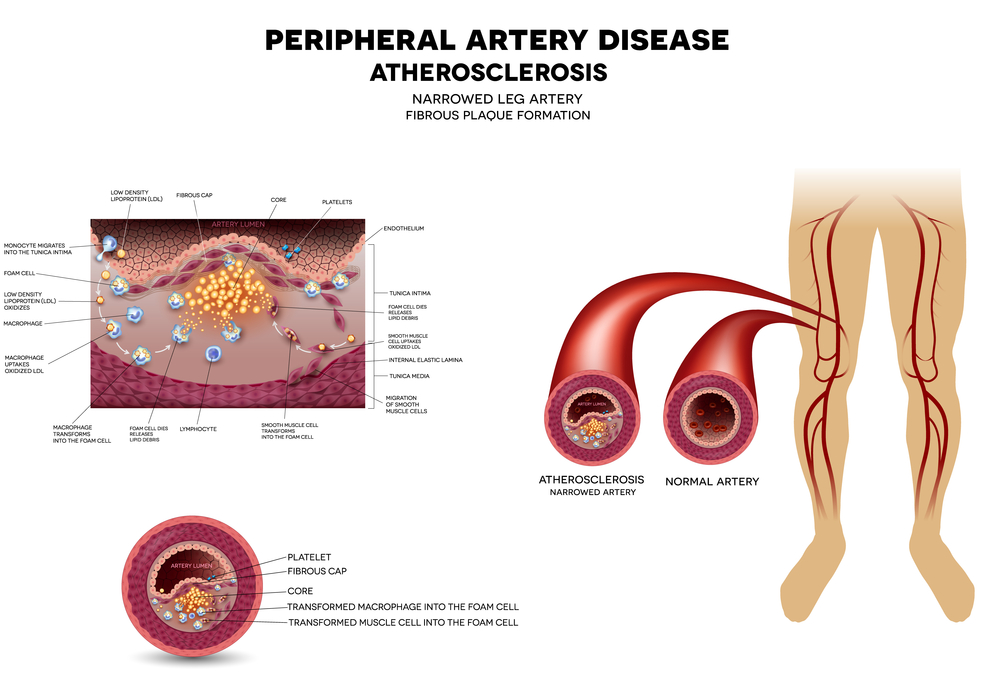
What are risk factors for P.A.D?
- If you smoke, you have an especially high risk for P.A.D.
- If you have diabetes, you have an especially high risk for P.A.D.
- People with high blood pressure, high cholesterol or are obese you are at risk for P.A.D.
- Your risk increases with age.
What are treatments for P.A.D?
- Tobacco cessation is highly recommended
- Some patients require minimally invasive procedures or surgery
- Angioplasty
- Stenting
- TPA treatment
- Atherectomy
- Bypass surgery
- You may be prescribed medication to treat high blood pressure/high cholesterol
- You may be put on blood thinners to help prevent clots
What tests can be done to check for P.A.D?
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI) Tab 1
- Doppler and Ultrasound (Duplex) imaging Tab 2
- Computed Tomographic Angiography (CT) Tab 3
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Tab 4
- Angiography Tab 5
Vasculuar Institute of Michigan

