Vascular Lab

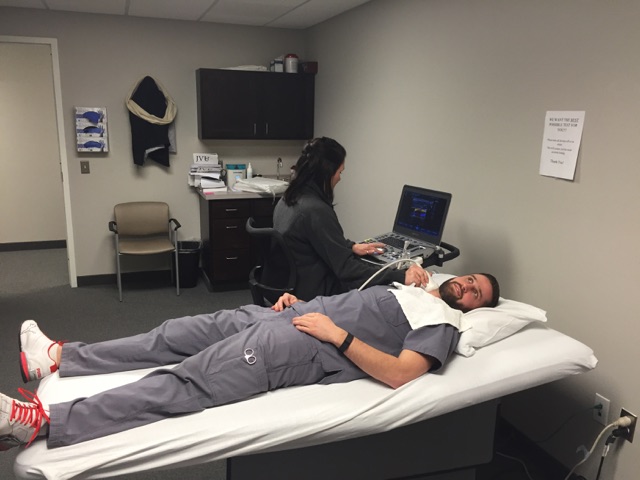
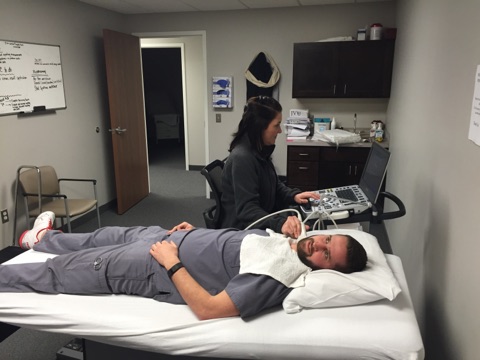
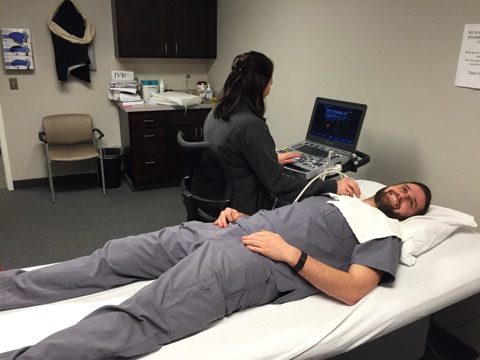
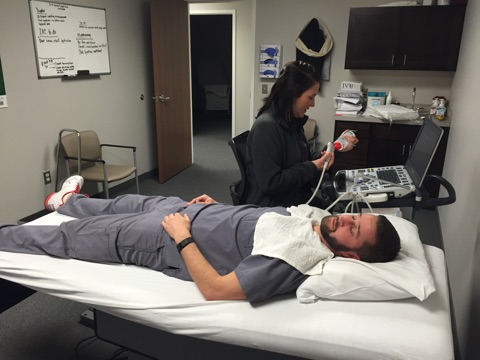
Vascular Institute of Michigan is proud to offer diagnostic testing here at our facility. Patients no longer have to be inconvenienced with multiple appointments at various facilities. VIM provides a one stop shop experience to our patients for all their vascular needs. Here at VIM we are empathetic with our patients and schedule your visit with the physician immediately following your testing. This way patients can be saved from paying multiple copays and visits and receive immediate results.
Certifications
- Physicians Tab 1
- Center Tab 2
Definitions
- Doppler Ultrasound Tab 1
- Ultrasound Imaging Tab 2
- Vascular Tech Tab 3
- Venous Ultrasound Tab 4
Tests
- Abdominal Aortic Screening Tab 1
- Arterial Doppler Tab 2
- Arterial Duplex Tab 3
- Cerebrovascular Duplex (Carotid Artery) Screening Tab 4
- Dialysis Access Screening Tab 5
- Renal and Mesenteric Artery Imaging Tab 6
- Venous Duplex Tab 7
- ABI/PVR Tab 8
An Abdominal Aorta Duplex uses ultrasound to evaluate the blood flow through the aorta. The aorta is the large artery that takes blood from the heart to the entire body. This non-invasive test does not use needles, drugs or dyes.
Exam:
Abdominal Aorta Duplex
Overview:
Gel is placed on the skin over the area to be studied. A hand held transducer, is used to make the pictures. The pictures will show the walls of the aorta and the blood flow through the aorta. Measurements will be taken to evaluate the size of the aorta. The doctor may order additional testing if this study is abnormal.
Purpose of Exam:
Evaluate the blood flow through the Aorta.
Special Instructions:
- Allow 1 hour for the test.
- Wear two-piece clothing.
- Take all of your regular medications with only a small sip of water, unless otherwise instructed by your physician.
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before the test.
- Your physician will be notified of the results.
An arterial Doppler is an exam of the arteries located in your arms or legs. It is a test that uses Doppler ultrasound to measure the blood pressures in the legs to make sure there is normal blood flow. The test is usually done when there intermittent claudication (leg pain on exercise) Doppler ultrasound can help vascular surgeon evaluate arterial blockages, such as plaque in arteries.
Exam:
Aterial Segmental Doppler
Risk Factors:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Elevated cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Family history of vascular disease
Symptoms:
- Leg pain that does not go away when you stop exercising
- Foot or toe wounds that won't heal or heal very slowly
- Gangrene
- A marked decrease in the temperature of your lower leg or foot particularly compared to the other leg or to the rest of your body
- Severe or steady aching or burning sensation in the toes, heel or foot can be very painful. Temporary relief is found by keeping the leg and foot down in a lowered position for a short period of time (the effect of gravity helps blood flow).
- As the disease gets worse, wounds and injuries might not heal and the skin becomes easily injured and starts to break down, leading to gangrene.
Overview:
Peripheral Circulation
The function of blood circulation is transportation – bringing food and oxygen to the body’s cells and organs. As the heart pumps the blood, the arteries serve as highways to carry the blood away from the heart. The arteries must be open in order to keep the body’s cells alive and healthy. “Peripheral” means the arteries that run along the arms and legs.
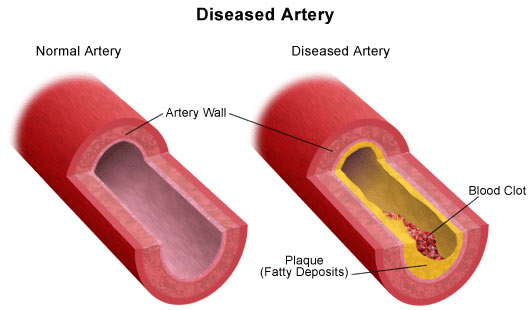
Atherosclerosis
The inside wall of a healthy artery is smooth and firm, where blood flows freely. As we age, the arteries may be affected by atherosclerosis – or “hardening of the arteries.” The inner lining of the artery gets thick and rough, with a buildup of cholesterol or fat, like rust in a pipe. This buildup is called “plaque,” and it can cause the artery to become narrow or even close off completely which could reduce or stop blood flow. Atherosclerosis can occur in all arteries, but the ones in the heart, neck, and legs are the most commonly affected.
During the exam
The exam is not painful; there are no needles, catheters or dyes used. There are no X-rays. The test has no side effects. The exam uses ultrasound to listen to your blood flow.
You will be lying on a bed, and you will be asked to remove your clothing from the waist down for a better examination of your legs. The technician will ask you several questions about the reasons your physician ordered the exam.
Recordings of the arterial flow in the upper or lower extremities will be taken by placing a small, smooth probe over parts of your arms and legs. This will determine whether a serious blockage is present in the large arteries. The circulation to your feet and toes also will be examined.
Your physician will receive a written interpretation of the test results within two to three days, and the physician will tell you what you should do next. The ultrasound tech will notify your physician immediately with the results if they notice a potentially serious problem.
Purpose of Exam:
If your doctor suspects you might have peripheral arterial occlusive disease, blockage of the arteries, he or she may order an arterial Doppler exam to confirm the diagnosis.
Risks of Exam:
There is no radiation used and generally no discomfort from the application of the ultrasound transducer to the skin. Blood pressure cuffs are used and may cause mild discomfort when inflated. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your doctor prior to the procedure.
Special Instructions:
Wear comfortable clothing that is easily removed before testing. Testing is approximately 45-60 minutes.
Arterial duplex scan is a painless exam that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to capture internal images of the major arteries in the arms, legs and neck.
Exam:
Aterial Duplex
Risk Factors:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Elevated cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Family history of vascular disease
Symptoms:
- Leg pain that does not go away when you stop exercising
- Foot or toe wounds that won't heal or heal very slowly
- Gangrene
- A marked decrease in the temperature of your lower leg or foot particularly compared to the other leg or to the rest of your body
- Severe or steady aching or burning sensation in the toes, heel or foot can be very painful. Temporary relief is found by keeping the leg and foot down in a lowered position for a short period of time (the effect of gravity helps blood flow).
- As the disease gets worse, wounds and injuries might not heal and the skin becomes easily injured and starts to break down, leading to gangrene.
Overview:
The exam uses ultrasound to look at the inside of your arteries and evaluate blood flow.
You will be lying on a bed, and you will be asked to remove your clothing from the waist down for a better examination of your legs. The technician will ask you several questions about the reasons your physician ordered the exam.
Images of the arteries and blood flow in the upper or lower extremities will be taken by placing gel and an ultrasound probe over parts of your arms and legs. This will determine whether a serious blockage is present in the large arteries.
Purpose of Exam:
Measures plaque in vessels and increased velocities suggesting a significant blockage
Special Instructions:
Wear comfortable, easily removable clothing. Testing is approximately 60-90 minutes.
Your carotid arteries are the two large blood vessels in your neck that supply blood to your brain. When these arteries become clogged with cholesterol, they become dangerously narrow. If a blood clot occurs in the carotid arteries, then blood cannot reach your brain and a stroke can result.
Exam:
Extracranial Carotid Duplex
Overview:
A carotid artery duplex scan is a type of vascular ultrasound study done to assess the blood flow of the arteries that supply blood from the heart through the neck to the brain.
A carotid artery duplex scan is a noninvasive (the skin is not pierced) procedure. The term "duplex" refers to the fact that 2 modes of ultrasound are used; Doppler and B-mode. The B-mode transducer (like a microphone) obtains an image of the carotid artery being studied. The Doppler probe within the transducer evaluates the velocity and direction of blood flow in the vessel.
A probe (also called a transducer) sends out ultrasonic sound waves at a frequency too high to be heard. When the probe is placed on the carotid arteries at certain locations and angles, the ultrasonic sound waves move through the skin and other body tissues to the blood vessels, where the waves echo off of the blood cells. The transducer picks up the reflected waves and sends them to an amplifier, which makes the ultrasonic sound waves audible. Absence or faintness of these sounds may indicate an obstruction to the blood flow.
A related procedure that may be performed to further evaluate the carotid artery and its branches is either a magnetic resonance arteriogram (MRA) or a carotid arteriogram, which is more invasive.
Purpose of Exam:
A carotid artery duplex scan is used to assess occlusion (blockage) or stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid arteries of the neck and/or the branches of the carotid artery. Plaque (a buildup of fatty materials), thrombus (blood clot), and other substances in the blood stream may cause a disturbance in the blood flow through the carotid arteries.
When the carotid arteries become blocked, symptoms may include dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, headache, momentary blindness in one eye, and/or a brief loss of ability to speak or move. These symptoms may indicate early warning signs of a possible stroke (brain attack, or cerebrovascular accident [CVA]).
A carotid artery duplex scan may also be performed when no symptoms of occlusion are present, yet an abnormal blood flow sound called a bruit (pronounced "BROO-ee") is heard with a stethoscope over the artery. This may indicate a possible condition of abnormal blood flow in the artery.
Additional reasons for the procedure include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Evaluation of previous procedures to restore blood flow to the area (such as an angioplasty to open up an artery that was blocked or surgery to bypass a blocked artery)
- Evaluation of carotid blood flow prior to a major cardiovascular surgical procedure, such as coronary artery bypass grafting or heart valve repair or replacement
- Location of a hematoma (a collection of clotted blood that may slow and eventually stop blood flow)
- Detect dissection of the carotid artery, a split between layers of the artery wall that may lead to obstruction of blood flow or a weakening of the wall of the artery
Special Instructions:
- Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
- You may be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
- Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting or sedation, is required.
- Your doctor may give you specific instructions about smoking and consuming caffeine. You may be asked to refrain from smoking for at least 2 hours before the test, as smoking causes blood vessels to constrict. You may also be asked to refrain from consuming caffeine in any form for about 2 hours prior to the test.
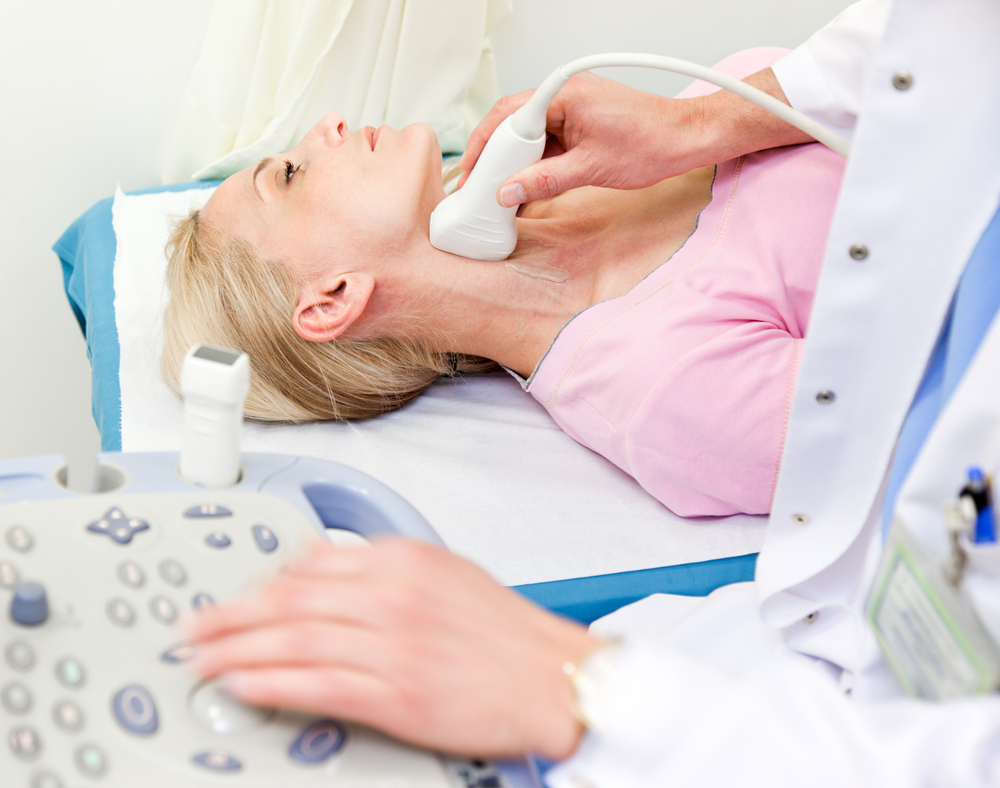
Generally, a carotid artery duplex scan follows this process:
- You will be asked to remove any clothing, jewelry, or other objects that may interfere with the scan.
- If you are asked to remove clothing, you will be given a gown to wear.
- You will lie on an examination table with your neck slightly extended (bent backward).
- A clear gel will be placed on the skin at various locations on the carotid arteries.
- The Doppler transducer will be pressed against the skin and moved around over the area of the artery being studied.
- When blood flow is detected, you will hear a "whoosh, whoosh" sound. The probe will be moved around to compare blood flow in different areas of the artery. Both sides of the neck will be examined.
- Once the procedure has been completed, the gel will be wiped off.
Testing done pre-operatively to determine suitability of the veins and arteries for dialysis access (AVF or AVG) placement in the upper or lower extremities.
Exam:
Vein Mapping for Arteriovenous Fistula/Graft Access
Overview:
Assessment of size, location, and major branches of the Greater Saphenous, Short Saphenous, Cephalic, and Basilic veins using gel and an ultrasound to obtain images. In the setting of AV fistula planning, a tourniquet should applied to the patient’s arm and the vein remeasured. The larger of the diameters (with or without the tourniquet applied) will then be recorded on the worksheet. The outer to outer diameter of the distal Brachial artery (just above the elbow) and Radial artery (at wrist) is also measured in the setting of fistula planning.
Purpose of Exam:
Determine diameter, length and suitability of the superficial veins for placement of dialysis access fistula or graft.
Special Instructions:
The test takes 30 to 60 minutes to complete. Consider wearing an undershirt, such as a tank top, as the full arm will need to be exposed. Please plan to arrive about 15 minutes before your scheduled appointment to complete the registration process.
Exam:
Upper Extremity Arterial Doppler with Radial dependency testing
Overview:
Blood pressure cuffs are applied on both upper arms, forearms, and fingers. The ultrasound technician will use a Doppler machine to record waveforms of artery and finger. Cuffs are then inflated to obtain pressures within the Manual compression maneuvers are then done by the technician on the wrist. This instructs the physician whether the patient is dependent on one or both arteries that supply blood flow to the hand.
Purpose of Exam:
Evaluation of arteries for blood flow, blockage, and dependency.
Special Instructions:
The test takes 45 to 60 minutes to complete. Consider wearing an undershirt, such as a tank top, as the full arm will need to be exposed. Please plan to arrive about 15 minutes before your scheduled appointment to complete the registration process.
Dialysis Access Testing (AVF/AVG)
Ultrasound examination that is performed post-operatively on the arteriovenous fistula or graft to determine usability or for any blockages and narrowing that may occur.
Exam:
AV Fistula or Graft
Overview:
Once a dialysis access is placed your physician may order this test to check the status of your access and if functioning appropriately. Arteriovenous access will typically have a thrill or vibration due to turbulent flow within the graft or vein.
Changes in the thrill may indicate a problem with the graft. A weak thrill can denote poor arterial inflow or arterial stenosis. Feeling a pulse rather than a thrill may signify high-grade stenosis at the outflow of an AVF or at the venous anastomosis of an AVG. Furthermore, significant increase in venous pressure during dialysis can indicate a stenosis at the venous anastomosis or outflow vein.
Once the AVF or AVG has been placed is it important to attend your regularly scheduled ultrasound appointments to evaluate for maturation, patency, and to rule out any narrowing or blockage. The exam uses ultrasound to look at the inside of your dialysis access and evaluate blood flow.
You will be lying on a bed, and you may be asked to remove your clothing from the site of the access. The technician will ask you several questions about the reasons your physician ordered the exam or any problems you may be experiencing. Images of the fistula or graft, and blood flow, will be taken by placing gel and an ultrasound probe over the entire access site. This will determine whether the access has matured and is ready for use, or a serious blockage is present.
Purpose of Exam:
Determine size and velocity of hemodialysis access or any narrowing that may be present.
Special Instructions:
The test takes 30 to 60 minutes to complete. Consider wearing an undershirt, such as a tank top, as the full arm will need to be exposed. Please plan to arrive about 15 minutes before your scheduled appointment to complete the registration process.
These tests examine the intestinal and kidney arteries. Plaque in these arteries can occasionally cause abdominal pain and in the case of kidney artery blockage, can lead to severe high blood pressure.
Exam:
Renal Artery Duplex
Overview:
A Renal Artery Duplex is an ultrasound test that uses high frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to examine the renal arteries. The renal arteries deliver blood to the kidneys.
Purpose of Exam:
Measure the blood flow.
Exam:
Mesenteric Artery Duplex
Overview:
Ultrasound evaluation of the arteries that supply blood flow to the organs that are involved in food digestion. If there is not enough blood flow to help digest your food, you may feel abdominal pain or cramping after eating a meal.
This test is done while you are lying on your back. Ultrasound gel is placed over your abdominal area that allows the ultrasound signals to travel to the mesenteric arteries. The technologist will use a transducer over the gel to visualize the mesenteric arteries. The technologist will use a transducer over the gel to visualize the mesenteric arteries. The ultrasound waves will bounce off of the blood vessels and travel back to the transducer, which produces the image on the ultrasound machine.
Purpose of Exam:
Visualize any area of narrowing in the artery and take measurements of the blood flow. You will hear a “swooshing” sound when the Doppler is turned on which represents your blood flow.
Special Instructions:
Wear loose, comfortable, easily removable clothing to your testing appointment. Testing is approximately 45-60 minutes. Avoid eating, drinking, chewing gum, and smoking for 6-8 hours prior to the test or overnight prior to the day of the test. It is very important to follow the preparation instructions to receive accurate testing results.
A duplex ultrasound is a test to see how blood moves through your arteries and veins.
Exam:
Venous Duplex for DVT
Overview:
Diagnosis and evaluation of the upper and lower extremity veins
Purpose of Exam:
Determine the presence of blood clots
Exam:
Venous Duplex for Venous Reflux (Varicose Veins)
Overview:
Imaging and testing of veins
Purpose of Exam:
Determine insufficiency of deep and superficial veins
A Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) study is a noninvasive vascular test in which blood pressure cuffs and a hand-held ultrasound device (called a Doppler or transducer) are used to obtain information about arterial blood flow in the arms and legs. Noninvasive means the procedure does not require the use of needles, dyes, radiation or anesthesia. The blood pressure cuffs and Doppler are used to determine the presence, severity and general location of peripheral arterial occlusive disease.
A PVR may also be called a vascular study or Doppler segmental pressure study.
Exam:
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
Overview:
The ABI is a measurement of the blood pressure in the lower leg compared to the blood pressure in the arm. Your physician will compare the two numbers to determine your ABI. Normally, the blood pressures in your ankle and arm should be about equal. But if your ankle pressure is half your arm pressure (or lower), it could be a sign that your leg arteries are narrowed.
The blood pressure cuffs are placed on the arm and leg and inflated, while the Doppler is used to listen to the blood flow in the leg and arm.
Purpose of Exam:
Evaluate the blood flow in your legs. Exam helps your physician diagnose arterial disease in the legs, but it does not identify which arteries are blocked.
Special Instructions:
The test takes 30 to 90 minutes to complete. Please plan to arrive about 15 minutes before your scheduled appointment to complete the registration process.
Exam:
Thoracic Outlet Testing
Overview:
During thoracic outlet testing, blood pressure cuffs are placed on the patient’s upper arms. The test is performed while the patient is sitting in a chair. The technologist will move the patient’s arms in different positions and take a blood pressure measurement at each position.
Purpose of Exam:
Evaluate the blood flow in your arms. Exam helps your physician diagnose arterial disease in the arms, but it does not identify which arteries are blocked.
Special Instructions:
The test takes 30 to 90 minutes to complete. Please plan to arrive about 15 minutes before your scheduled appointment to complete the registration process.
Vasculuar Institute of Michigan

